-
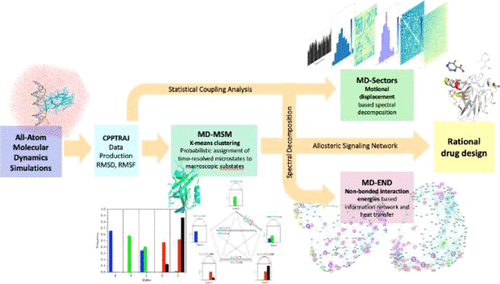 Insights into Rational Design of a New Class of Allosteric Effectors with Molecular Dynamics
Insights into Rational Design of a New Class of Allosteric Effectors with Molecular Dynamics
Han ISM, Abramson D*, Thayer KM.
Markov State Models and Network Theory.
ACS Omega,7(2831) (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05624.
The development of drugs to restore protein function has been a major advance facilitated by molecular medicine. Allosteric regulation, a phenomenon widely observed in nature, in which a molecule binds to control a distance active site, holds great promise for regulating proteins, yet how to rationally design such a molecule remains a mystery.
-
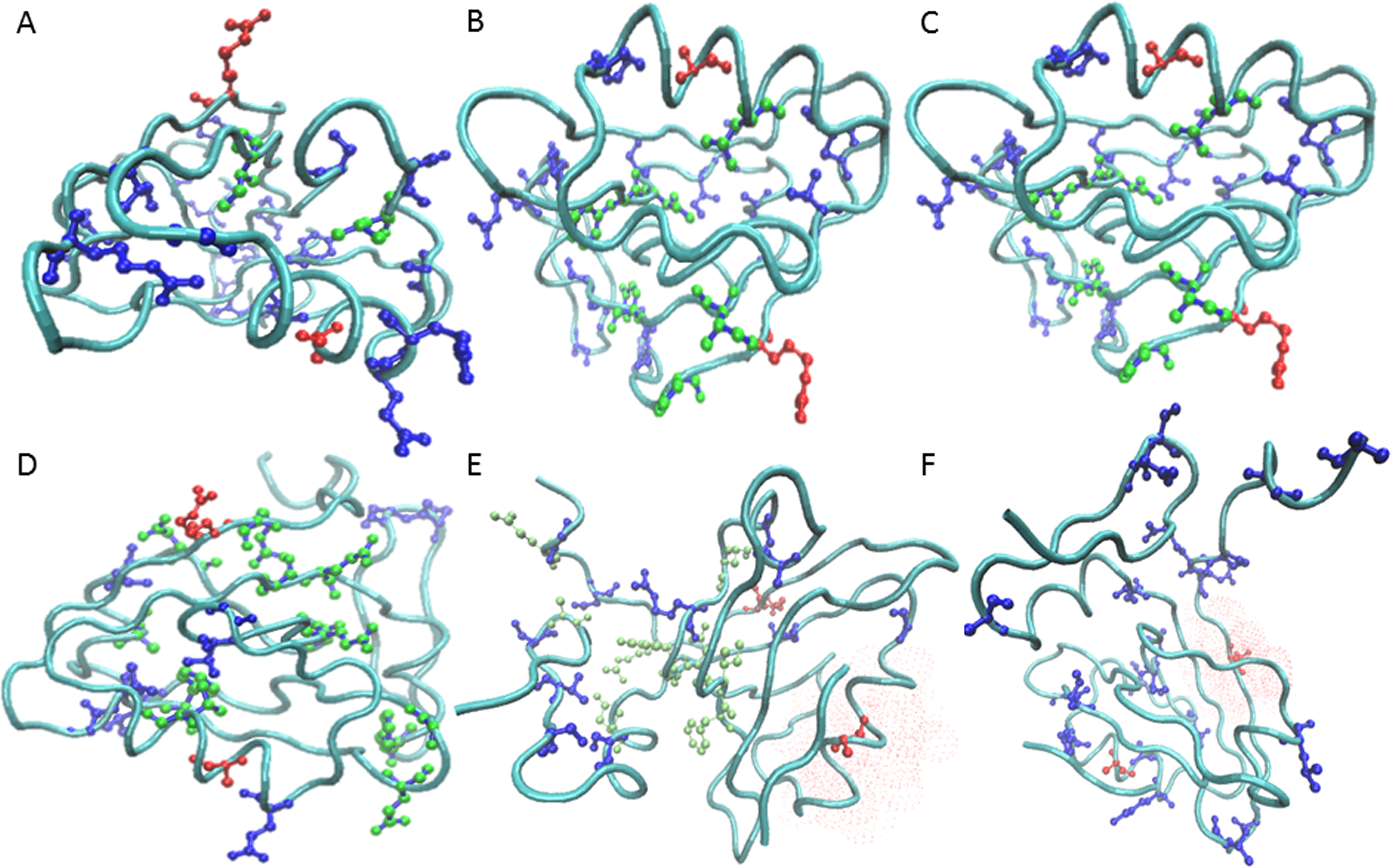 Dependence of prevalence of contiguous pathways in proteins on structural complexity.
Dependence of prevalence of contiguous pathways in proteins on structural complexity.
Thayer KM, Galganov JC*, Stein AJ*.
PLoS ONE, 12, e0188616 (2017). DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0188616
Allostery is a regulatory mechanism in proteins where an effector molecule binds distal from an active site to modulate its activity. Allosteric signaling may occur via a continuous path of residues linking the active and allosteric sites, which has been suggested by large conformational changes evident in crystal structures. An alternate possibility is that the signal occurs in the realm of ensemble dynamics via an energy landscape change. While the latter was first proposed on theoretical grounds, increasing evidence suggests that such a control mechanism is plausible.
-
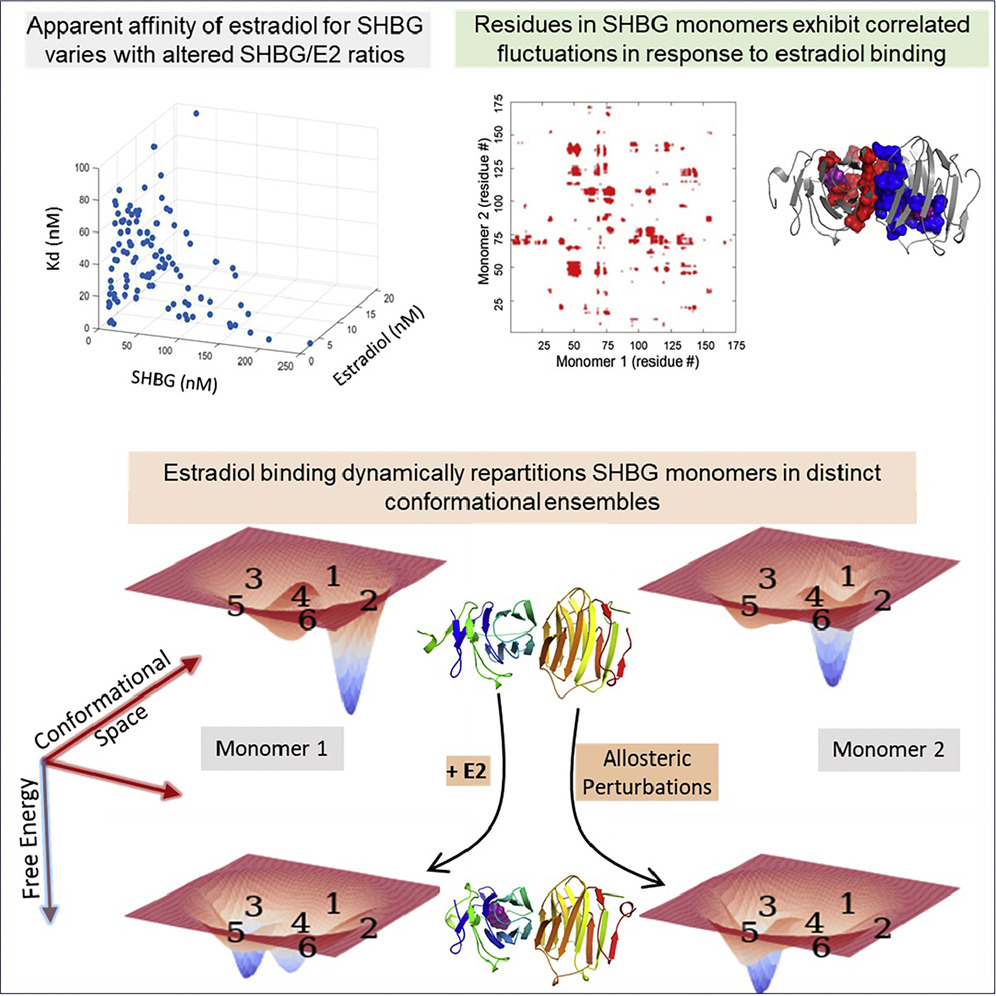 Estradiol Binding Induces Allosteric Coupling and Partitioning of Sex Hormone Binding
Estradiol Binding Induces Allosteric Coupling and Partitioning of Sex Hormone Binding
Jasuja R, Spencer DJ, Jayaraj A, Peng L, Krishna M, Lawney B, Patel P, Jayaram B, Thayer KM,
Beveridge DL, Bhasin S.
Globulin Monomers Among Various Conformational States.
iScience, 24(102424) (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102414
Sex-hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) regulates the transport and bioavailability of estradiol. The dynamics of estradiol's binding to SHBG are incompletely understood, although it is believed that estradiol binds to each monomer of SHBG dimer with identical affinity (Kd ∼2 nM). Contrary to the prevalent view, we show that estradiol's binding to SHBG is nonlinear, and the "apparent" Kd changes with varying estradiol and SHBG concentrations.
-
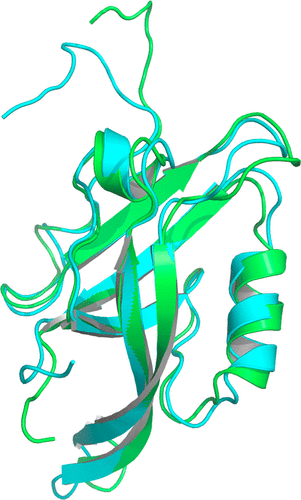 A Molecular Dynamics-Markov State Model of Protein Ligand Binding and Allostery in CRIB-PDZ: Conformational Selection and Induced Fit.
A Molecular Dynamics-Markov State Model of Protein Ligand Binding and Allostery in CRIB-PDZ: Conformational Selection and Induced Fit.
Thayer KM, Lakhani B, and Beveridge DL.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B.,121, 5509-5514 (2017). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b02083
Conformational selection and induced fit are well-known contributors to ligand binding and allosteric effects in proteins. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations now enable the theoretical study of protein–ligand binding in terms of ensembles of interconverting microstates and the population shifts characteristic of “dynamical allostery.” Here we investigate protein–ligand binding and allostery based on a Markov state model (MSM) with states and rates obtained from all-atom MD simulations.
 Insights into Rational Design of a New Class of Allosteric Effectors with Molecular Dynamics
Insights into Rational Design of a New Class of Allosteric Effectors with Molecular Dynamics Dependence of prevalence of contiguous pathways in proteins on structural complexity.
Dependence of prevalence of contiguous pathways in proteins on structural complexity. Estradiol Binding Induces Allosteric Coupling and Partitioning of Sex Hormone Binding
Estradiol Binding Induces Allosteric Coupling and Partitioning of Sex Hormone Binding A Molecular Dynamics-Markov State Model of Protein Ligand Binding and Allostery in CRIB-PDZ: Conformational Selection and Induced Fit.
A Molecular Dynamics-Markov State Model of Protein Ligand Binding and Allostery in CRIB-PDZ: Conformational Selection and Induced Fit.